

Six weeks after your surgery, you may stop wearing the removable splint. You will start your physical therapy to regain wrist function and strength after your first clinic visit. At that time, the splint will be removed and exchanged with a removable wrist splint. With an external fixator, most of the hardware remains outside of the body.Īfter the surgery, a splint will be placed for two weeks until your first follow-up visit. In these cases, an external fixator with or without additional wires may be used to secure the fracture. If there are multiple bone pieces, fixation with plates and screws may not be possible. Plates and screws will be used to hold the pieces in place. In certain cases, a second incision is required on the back side of your wrist to re-establish the anatomy. The pieces are put together and held in place with one or more plates and screws. Surgery is typically performed through an incision over the volar aspect of your wrist (where you feel your pulse).
This option is usually for fractures that are considered unstable or can’t be treated with a cast. Your orthopaedic surgeon will evaluate the fracture and decide whether you will need surgery or if the fracture can be treated with a cast for six weeks. The reduction (closed reduction) is usually performed with local anesthesia. Once it is anatomically aligned, a plaster splint or cast is applied.

They may be taken less often if the fracture was not reduced and thought to be stable.Ī displaced fracture needs to be corrected first. X-rays may be taken at three weeks and then at six weeks if the fracture was reduced or thought to be unstable. Once the cast is removed, you can start physical therapy to regain proper wrist function and strength. Then you will be given a removable wrist splint to wear for comfort and support. Usually a cast will remain on for up to six weeks. It often serves as a final treatment until the bone heals. If the distal radius fracture is in a good position, a splint or cast is applied. Fracture reduction is performed under local anesthesia, which means only the painful area is numbed. If the fracture is displaced, it is reduced (put back into the correct position) before it is placed in a splint. In any case, the immediate fracture treatment is the application of a splint for comfort and pain control.
#Distal radius fracture how to#
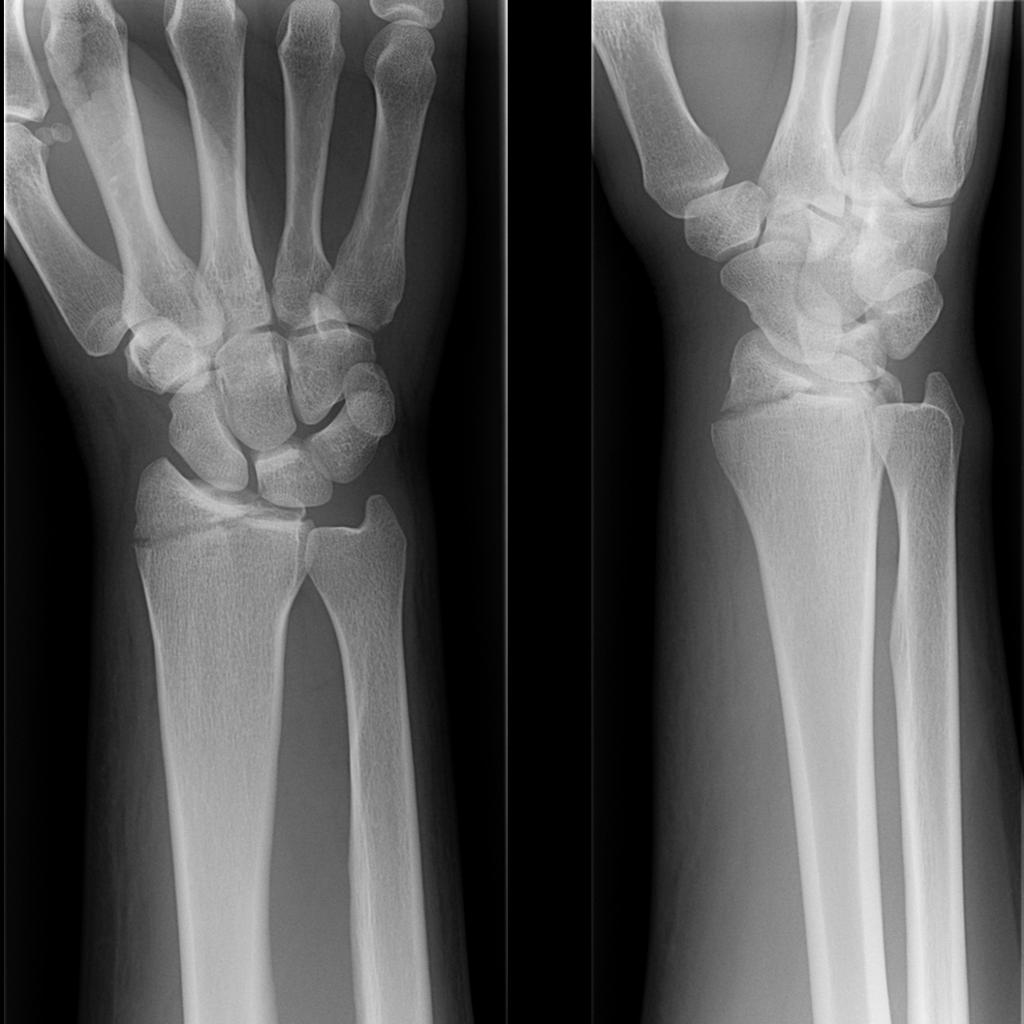
What is the treatment for a distal radius fracture?ĭecisions on how to treat a distal radius fracture may depend on many factors, including: Deformity - the wrist being in an odd position.Immediate pain with tenderness when touched.What are the symptoms of a distal radius fracture? This usually makes for a distinct drop in the wrist where the longer part of the radius ends. The end of the distal radius typically shifts down toward the palm side in this type of fracture. It may result from an impact to the back of the wrist, such as falling on a bent wrist. A Smith fracture is the less common of the two.It happens because the broken end of the distal radius shifts up toward the back of the hand. There is a distinct “bump” in the wrist similar to the neck of the fork. The side view of a wrist after a Colles fracture is sometimes compared to the shape of a fork facing down. A Colles fracture may result from direct impact to the palm, like if you use your hands to break up a fall and land on the palms.In these cases, the injury is called a distal radius and ulna fracture.ĭepending on the angle of the distal radius as it breaks, the fracture is called a Colles or Smith fracture. It can also occur along with a fracture of the distal ulna (the forearm bone on the small finger side).

It can also happen in a car accident, a bike accident, a skiing accident or another sports activity.Ī distal radius fracture can be isolated, which means no other fractures are involved. The break usually happens due to falling on an outstretched or flexed hand. When the radius breaks near the wrist, it is called a distal radius fracture. The part of the radius connected to the wrist joint is called the distal radius. The radius is one of two forearm bones and is located on the thumb side.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
